CoreLocation
iOS8.0之前的定位
import UIKit
import CoreLocation
class ViewController: UIViewController {
lazy var locationM: CLLocationManager = {
let locationM = CLLocationManager()
locationM.delegate = self
return locationM
}()
override func touchesBegan(touches: Set<UITouch>, withEvent event: UIEvent?) {
// 从ios6.0以后, 只要我们在app内部, 使用了用户隐私(照片 通讯录), 系统就会自动弹框 让个用户进行授权, 如果用户不同意, 就意味着, 你基本上没有机会再获取用户隐私
// 获取用户位置信息
// 1. 创建位置管理者
// locationM = CLLocationManager()
//
// // 1.1 block, 代理, 通知,
// locationM.delegate = self
// 2. 实用位置管理者, 开始获取用户位置信息
// 小经验: 如果以后实用位置管理者这个对象, 实现某个服务, 那么可以以startXX 开始某个服务 以 stopXX停止某个服务
// 开始更新位置信息 ing, 意味着, 一旦调用了这个方法, 就会不断的刷新用户位置, 然后高武外界
locationM.startUpdatingLocation()
}
}
extension ViewController: CLLocationManagerDelegate {
/**
定位到之后调用的方法
- parameter manager: 位置管理者
- parameter locations: 位置对象数组
*/
func locationManager(manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) {
print("获取到位置")
}
}
iOS8.0之后的定位
import UIKit
import CoreLocation
class ViewController: UIViewController {
// 如果是ios8.0以后, 在想请求用户的位置信息, 需要主动的请求授权, 系统不会再自动弹出一个窗口
lazy var locationM: CLLocationManager = {
let locationM = CLLocationManager()
locationM.delegate = self
if #available(iOS 8.0,*) {
// 请求的是前台定位授权
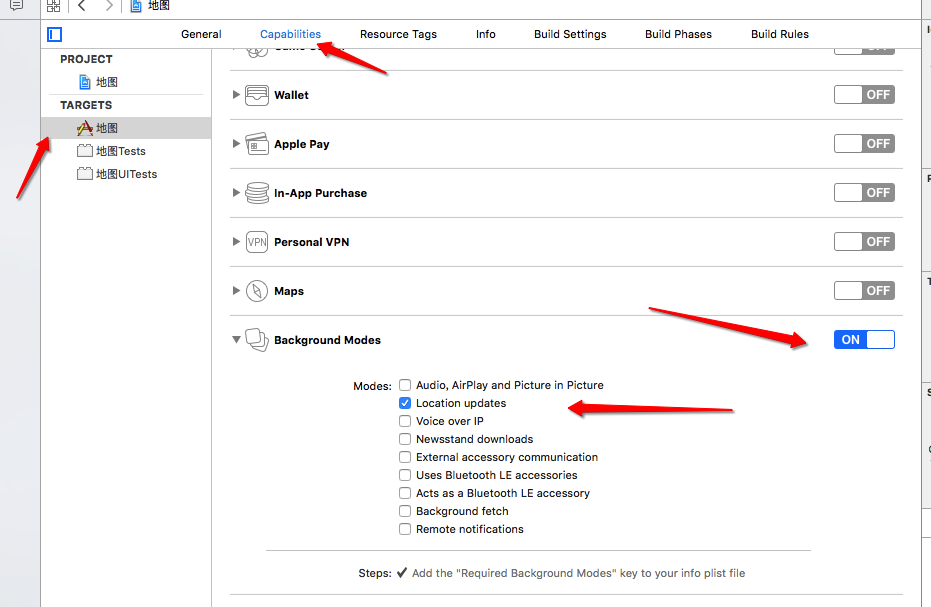
//默认情况,只能在前台获取位置信息,如果想后台也获取位置信息,需要勾选后台模式location updates
//虽然可以在后台获取位置信息,但是界面上方会闪动蓝色横幅
locationM.requestWhenInUseAuthorization()
}
if #available(iOS 8.0,*) {
// 前后台定位授权
//默认情况,能同时在前后台获取位置信息,不需要勾选后台模式location updates
//不会在界面上方会闪动蓝色横幅
// locationM.requestAlwaysAuthorization()
}
return locationM
}()
override func touchesBegan(touches: Set<UITouch>, withEvent event: UIEvent?) {
locationM.startUpdatingLocation()
}
}
extension ViewController: CLLocationManagerDelegate {
func locationManager(manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) {
print("已经获取到位置信息")
}
}
IOS8.0之后,9.0之前和IOS9.0之后获取后台定位定位方法
方法1,代码设置
import UIKit
//1,导入CoreLocation
import CoreLocation
class ViewController: UIViewController {
//2,懒加载CLLocationManager
lazy var locationM : CLLocationManager = {
let locationM = CLLocationManager()
//3,设置代理
locationM.delegate = self
return locationM
}()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
//发送请求,调用该方法,只在App进入前台时候进行定位,并且需要在info.plist中加上NSLocationWhenInUseUsageDescription这个键,值随便填
if #available(iOS 8.0, *) {//版本设置
locationM.requestWhenInUseAuthorization()
}
//6,启动定位
locationM.startUpdatingLocation()
}
}
//遵守协议
extension ViewController : CLLocationManagerDelegate {
//4,实现代理方法
func locationManager(manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) {
print(locations)
print("-----")
}
}

方法二
import UIKit
//1,导入CoreLocation
import CoreLocation
class ViewController: UIViewController {
//2,懒加载CLLocationManager
lazy var locationM : CLLocationManager = {
let locationM = CLLocationManager()
//3,设置代理
locationM.delegate = self
return locationM
}()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
//发送请求,调用该方法,只在App进入前台时候进行定位,并且需要在info.plist中加上NSLocationWhenInUseUsageDescription这个键,值随便填
if #available(iOS 8.0, *) {
locationM.requestWhenInUseAuthorization()
if #available(iOS 9.0, *) {
//IOS9.0之后必须设置该属性为true,才能在Xcode里设置后台运行之后后台定位
locationM.allowsBackgroundLocationUpdates = true
}
}
//6,启动定位
locationM.startUpdatingLocation()
}
}
//遵守协议
extension ViewController : CLLocationManagerDelegate {
//4,实现代理方法
func locationManager(manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) {
print(locations)
print("-----")
}
}
CLLocationManagerDelegate下监测定位服务状态的代理方法
func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didChangeAuthorization status: CLAuthorizationStatus) {
var info:String = ""
switch status {
case .authorizedAlways:
info = "前后台定位授权"
case .authorizedWhenInUse:
info = "前台定位授权"
case .denied:
// 判断当前设备是否支持定位, 并且定位服务是否开启
if CLLocationManager.locationServicesEnabled() {
info = "功能被用户拒绝"
// 手动通过代码, 来跳转到设置界面
if #available(iOS 8.0, *) {
let url = URL(string: UIApplicationOpenSettingsURLString)
if UIApplication.shared.canOpenURL(url! as URL) {
UIApplication.shared.openURL(url! as URL)
}
}
}
else {
// 当我们在app内部想要访问用户位置, 但是当前的定位服务是关闭状态, 那么系统会自动弹出一个窗口, 快捷跳转到设置界面, 让用户设置
info = "询问用户是否开启定位服务"
}
case .notDetermined:
info = "用户没有决定"
case .restricted:
info = "功能受限制"
default:
break
}
statusText.text = info
}
定位管理的一些参数设置
// 设置过滤距离
// 每隔100米定位一次
// 1 111KM/100M
// 如果最新的位置距离上一次的位置之间的物理距离, 大于这个值, 就会通过代理来告诉我们最新的位置数据
locationM.distanceFilter = 100
// 定位精确度
// kCLLocationAccuracyBestForNavigation // 最适合导航
// kCLLocationAccuracyBest; // 最好的
// kCLLocationAccuracyNearestTenMeters; // 附近10米
// kCLLocationAccuracyHundredMeters; // 附近100米
// kCLLocationAccuracyKilometer; // 附近1000米
// kCLLocationAccuracyThreeKilometers; // 附近3000米
// 经验: 如果定位的精确度越高, 那么越耗电, 而且定位时间越长
//
locationM.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyBest
定位服务的类型
// 定位: 标准定位服务 (gps/wifi/蓝牙/基站)
locationM.startUpdatingLocation()
// 显著位置变化的服务(基站进行定位, 电话模块)
locationM.startMonitoringSignificantLocationChanges()
requestLocation()方法,一般不使用
if #available(iOS 9.0, *) {
// 定位逻辑
// 定位精确度
// kCLLocationAccuracyBestForNavigation // 最适合导航
// kCLLocationAccuracyBest; // 最好的
// kCLLocationAccuracyNearestTenMeters; // 附近10米
// kCLLocationAccuracyHundredMeters; // 附近100米
// kCLLocationAccuracyKilometer; // 附近1000米
// kCLLocationAccuracyThreeKilometers; // 附近3000米
// 不能与 startUpdatingLocation同时使用
// 必须实现代理的定位失败的方法 func locationManager(manager: CLLocationManager, didFailWithError error: NSError)
locationM.requestLocation()
}
当定位到之后调用的代理方法 locationManager(manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation])
locations:
[<+44.15118730,+87.96232247> +/- 65.00m (speed -1.00 mps / course -1.00) @ 2017/1/25 中国标准时间 20:47:04]
/**
- parameter manager: 位置管理者
- parameter locations: 位置数组
*/
func locationManager(manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) {
let newLocation = locations.last
// CLLocation
// coordinate: 经纬度信息
// altitude: 海拔信息
// horizontalAccuracy: 如果整个数字是负数, 就代表位置数据无效
// verticalAccuracy: 如果整个数字是负数, 就代表海拔数据无效
// course: 航向
// speed: 速度
// distance: 计算两个经纬度坐标之间的物理指向距离
print(newLocation)
}
计算位移方向和位移距离实例
例如:”北偏东 30度 方向,移动了 8米”
import UIKit
import CoreLocation
class ViewController: UIViewController {
var oldLocation:CLLocation?
let angleStrs:[String] = ["北偏东","东偏南","南偏西","西偏北"]
lazy var locationM: CLLocationManager = {
let lm = CLLocationManager()
lm.delegate = self
return lm
}()
override func touchesBegan(_ touches: Set<UITouch>, with event: UIEvent?) {
locationM.startUpdatingLocation()
}
}
extension ViewController: CLLocationManagerDelegate {
func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) {
guard let newLocation = locations.last else {
return
}
// 1. 获取当前的行走航向
let index = Int(newLocation.course) / 90
var angleStr = angleStrs[index]
// 2. 行走的偏离角度
let angle = newLocation.course.truncatingRemainder(dividingBy: 90)
if Int(angle) == 0 {
let index = angleStr.index(angleStr.startIndex, offsetBy: 1)
angleStr = "正" + angleStr.substring(to: index)
}
// 3. 移动了多少米
let lastLocation = oldLocation ?? newLocation
let distance = newLocation.distance(from: lastLocation)
oldLocation = newLocation
// 4. 合并字符串, 打印
if Int(angle) == 0 {
print(angleStr + "方向, 移动了\(distance)米")
} else {
print(angleStr + "\(angle)" + "方向, 移动了\(distance)米")
}
}
}
区域监听
import UIKit
import CoreLocation
class ViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var infoLabel: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var identifiText: UITextField!
@IBOutlet weak var startBtn: UIButton!
@IBOutlet weak var coordinateLabel: UILabel!
var coordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2D?
var region:CLCircularRegion?
lazy var locationM:CLLocationManager = {
var lm:CLLocationManager = CLLocationManager()
lm.delegate = self
// 如果想要进行区域监听, 在ios8.0之后, 必须要请求用户的位置授权
if #available(iOS 8.0, *) {
lm.requestAlwaysAuthorization()
if #available(iOS 9.0, *) {
//IOS9.0之后必须设置该属性为true,才能在Xcode里设置后台运行之后后台定位
lm.allowsBackgroundLocationUpdates = true
}
}
return lm
}()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
locationM.startUpdatingLocation()
}
@IBAction func startTest(_ sender: Any) {
// 区域监听
// 1. 创建区域
let isTesting = startBtn.titleLabel?.text == "开始检测"
let center = coordinate!
let distance: CLLocationDistance = 200
region = CLCircularRegion(center: center, radius: distance, identifier: identifiText.text!)
guard let region = region else {
return
}
identifiText.isEnabled = !isTesting
if isTesting {
if CLLocationManager.isMonitoringAvailable(for: CLCircularRegion.self)
{
coordinateLabel.text = "维度:\(center.latitude),经度:\(center.longitude),地点名称:\(region.identifier)"
startBtn.setTitle("停止检测", for: .normal)
// 2. 监听区域
locationM.startMonitoring(for: region)
//请求某个区域的状态
locationM.requestState(for: region)
}
} else {
coordinateLabel.text = ""
startBtn.setTitle("开始检测", for: .normal)
locationM.stopMonitoring(for: region)
}
}
}
extension ViewController: CLLocationManagerDelegate {
func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) {
coordinate = locations.last?.coordinate
print(locations)
}
// 进入区域时调用
func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didEnterRegion region: CLRegion) {
infoLabel.text = "进入区域\(region.identifier)"
}
// 离开区域时调用
func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didExitRegion region: CLRegion) {
infoLabel.text = "进离开区域\(region.identifier)"
}
func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didDetermineState state: CLRegionState, for region: CLRegion) {
if region.identifier == identifiText.text {
if state == .inside {
infoLabel.text = "进入区域\(region.identifier)"
}else if state == .outside {
infoLabel.text = "进离开区域\(region.identifier)"
}
}
}
}
地理编码和反地理编码
import UIKit
import CoreLocation
class ViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var addressInput: UITextField!
@IBOutlet weak var coordinateLabel: UILabel!
//创建地理编码对象
lazy var geoCoder:CLGeocoder = CLGeocoder()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
}
//地理名称转定位信息
@IBAction func geocoding(_ sender: Any) {
geoCoder.geocodeAddressString(addressInput.text!) { (placemarks:[CLPlacemark]?, error:Error?) in
if error == nil {
print("地理编码成功")
}
else {
self.addressInput.text = "地理编码失败"
return
}
guard let placemarks = placemarks else {
return
}
guard let firstPlace = placemarks.first else {
return
}
print(firstPlace.location ?? "")
self.coordinateLabel.text = "维度:\(firstPlace.location!.coordinate.latitude) 经度:\(firstPlace.location!.coordinate.longitude)"
print(firstPlace.addressDictionary ?? "")
/**
[AnyHashable("Street"): 二楼段, AnyHashable("Country"): 中国, AnyHashable("City"): 昌吉回族自治州, AnyHashable("State"): 新疆维吾尔自治区, AnyHashable("Name"): 二楼段, AnyHashable("Thoroughfare"): 二楼段, AnyHashable("FormattedAddressLines"): <__NSArrayM 0x174442e20>(
中国新疆维吾尔自治区昌吉回族自治州昌吉市兵团军户农场二楼段
)
, AnyHashable("CountryCode"): CN, AnyHashable("SubLocality"): 昌吉市]
**/
guard let addressCountry:String = firstPlace.addressDictionary![AnyHashable("Country")] as? String else{
return
}
guard let addressCity:String = firstPlace.addressDictionary![AnyHashable("City")] as? String else{
return
}
guard let addressState:String = firstPlace.addressDictionary![AnyHashable("State")] as? String else{
return
}
guard let addressName:String = firstPlace.addressDictionary![AnyHashable("Name")] as? String else{
return
}
self.addressInput.text = "\(addressCountry)\(addressState)\(addressCity)\(addressName)"
print(addressName)
}
}
//定位信息转地理名称
@IBAction func reverseGeocoding(_ sender: Any) {
guard let locationStrs = self.addressInput.text?.components(separatedBy: ",") else {
print("locationStrs:\(self.addressInput.text ?? "无法分解的值")")
return
}
if locationStrs.count > 1 {
print(locationStrs as [String]);
//print(CGFloat(locationStrs[0]),CGFloat(locationStrs[1]))
let location = CLLocation(latitude: CLLocationDegrees(locationStrs[0])!, longitude:CLLocationDegrees(locationStrs[1])!)
geoCoder.reverseGeocodeLocation(location) { (placemarks:[CLPlacemark]?, error:Error?) in
if error == nil {
print("反地理编码成功")
}
else
{
self.addressInput.text = "输入的经纬度无效"
return
}
guard let placemarks = placemarks else {
return
}
guard let firstPlace = placemarks.first else {
return
}
print(firstPlace.location ?? "")
self.coordinateLabel.text = "维度:\(firstPlace.location!.coordinate.latitude) 经度:\(firstPlace.location!.coordinate.longitude)"
print(firstPlace.addressDictionary ?? "")
guard let addressCountry:String = firstPlace.addressDictionary![AnyHashable("Country")] as? String else{
return
}
guard let addressCity:String = firstPlace.addressDictionary![AnyHashable("City")] as? String else{
return
}
guard let addressState:String = firstPlace.addressDictionary![AnyHashable("State")] as? String else{
return
}
guard let addressName:String = firstPlace.addressDictionary![AnyHashable("Name")] as? String else{
return
}
self.addressInput.text = "\(addressCountry)\(addressState)\(addressCity)\(addressName)"
print(addressName)
}
}
}
}